The Microsoft Graph Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Table of Contents
On November 22nd, Microsoft announced that the Microsoft Graph CLI was now generally available at version 1.0.0. The command-line tool provides convenient methods to access Microsoft Graph API capabilities on any operating system and any shell. The CLI uses the Microsoft Graph v1.0 endpoint. Microsoft does provide a Beta CLI that interacts with the Microsoft Graph Beta endpoint.
The CLI not only allows you to get objects but update, create and delete objects using the Microsoft Graph REST API.
Download the CLI
MacOS
Download the CLI from here.
- If you have an ARM based Mac (M1, M2, etc) computer, download the
msgraph-beta-cli-osx-arm64...package. - If you have an Intel processor, download the
msgraph-beta-cli-osx-x64...package.
Extract the files to a directory you can reference later. For my purposes, I created a folder called, ‘MSGraph CLI’ in my Home Directory.
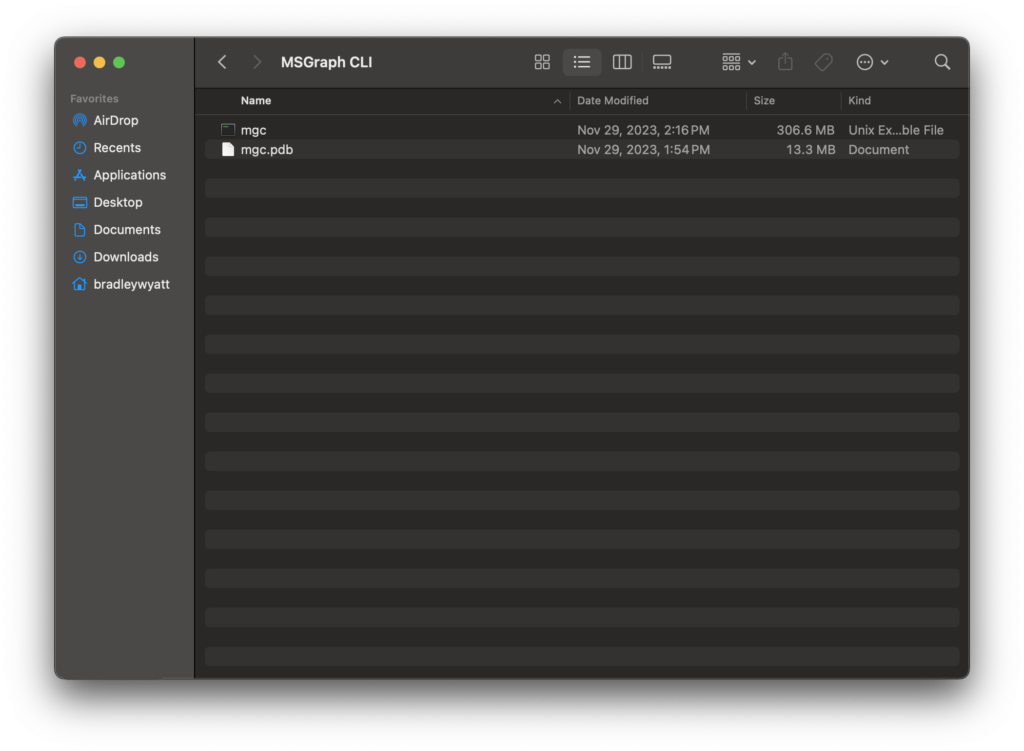
Next, we will update PATH permanently by editing your shell profile (~/.bash-profile or ~/.zsh-profile). In my case I am using zsh (z shell), so I opened Finder > Go > Go to Folder and entered in ~/.zsh-profile
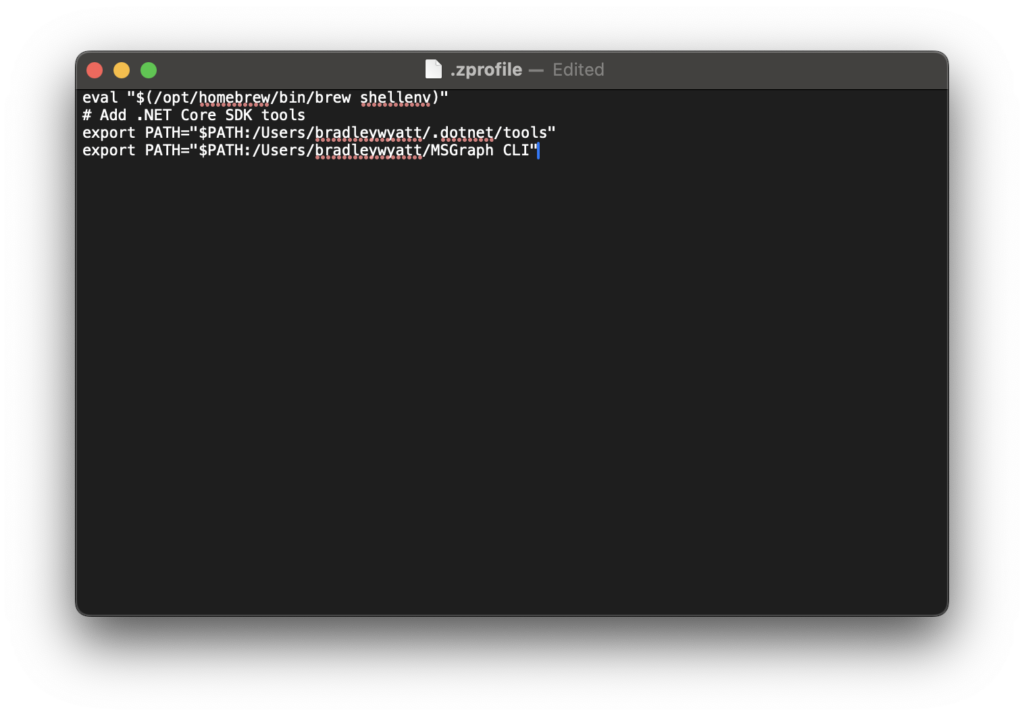
Add the following code to your profile
export PATH=$PATH:[path-to-the-cli-folder]Since mine is stored at ‘/home/bradleywyatt/MSGraph CLI‘ my profile is as follows:
Windows
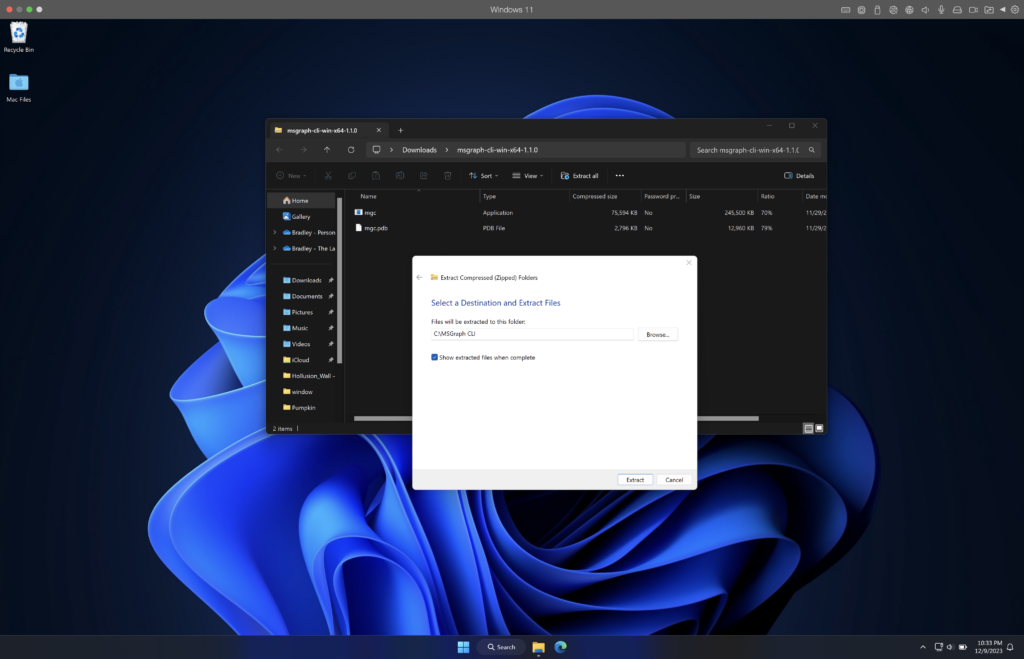
Download the CLI from here. Extract the files to a directory you can reference later. In my example, I created a folder called, ‘MSGraph CLI’ at the root of C:\
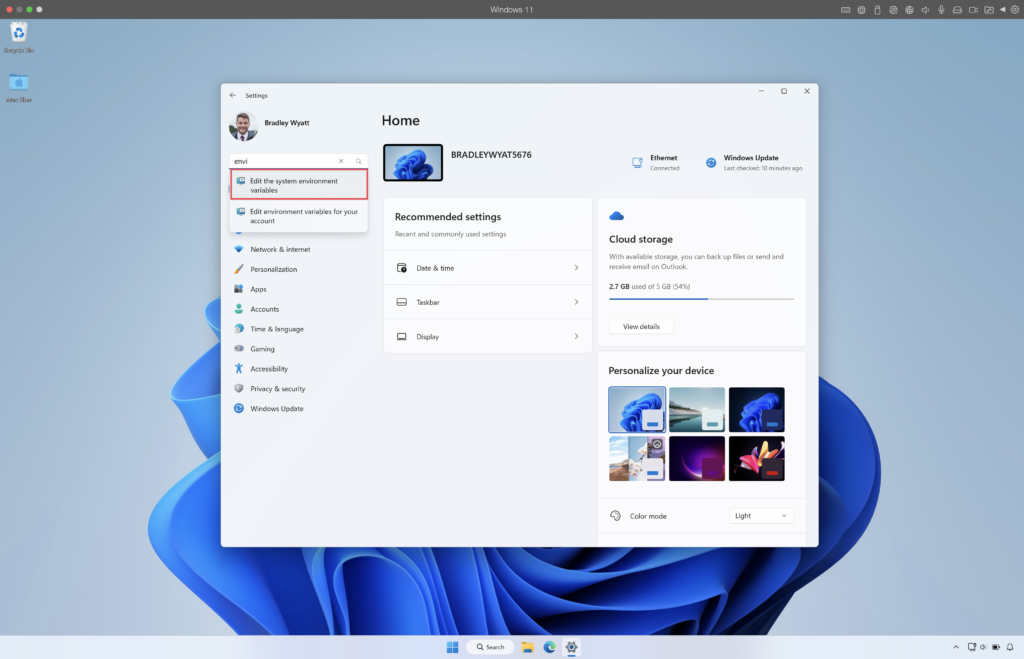
Next, open Settings and search “Environment” and select “Edit the system environment variables“
Click on “Environment variables” and then select, ‘Path‘ and ‘Edit‘
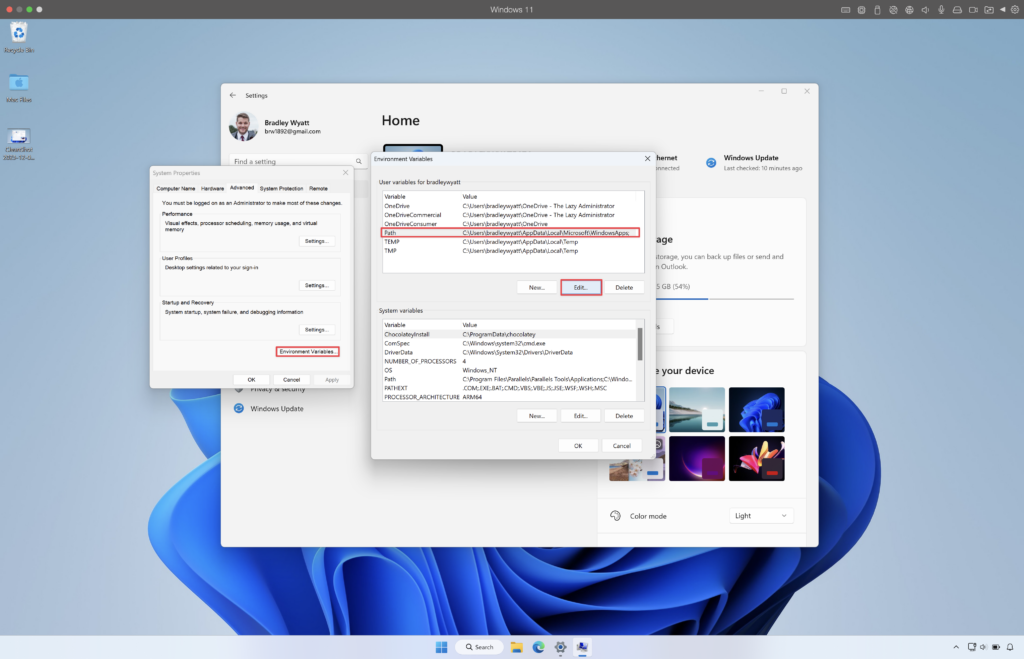
Add the full path to the directory containing mgc.exe. In my case I will add ‘C:\MSGraph CLI’
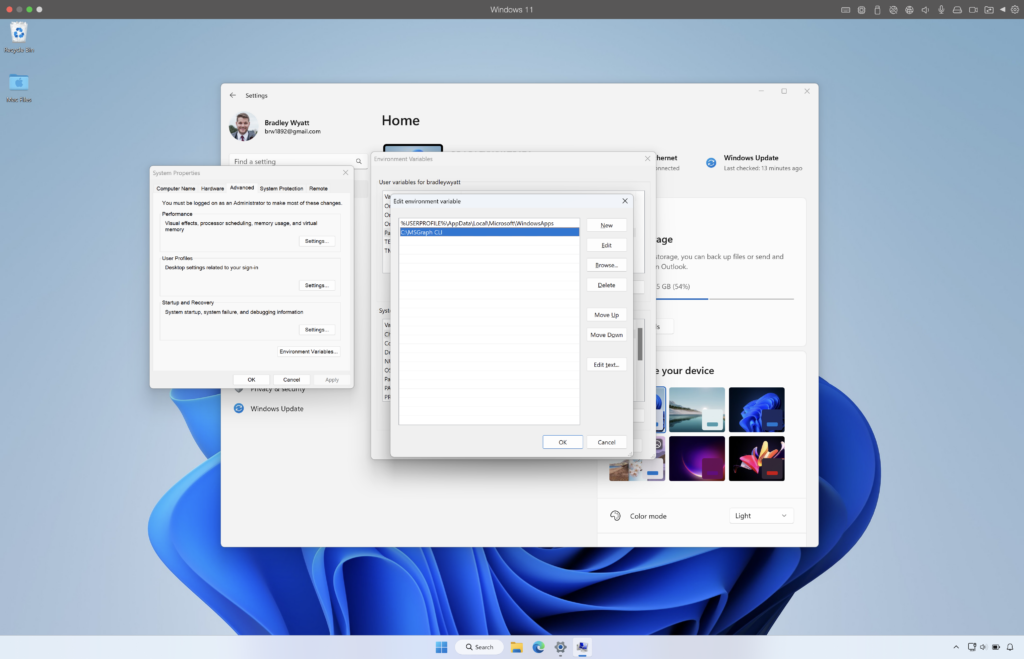
Verify the Installation
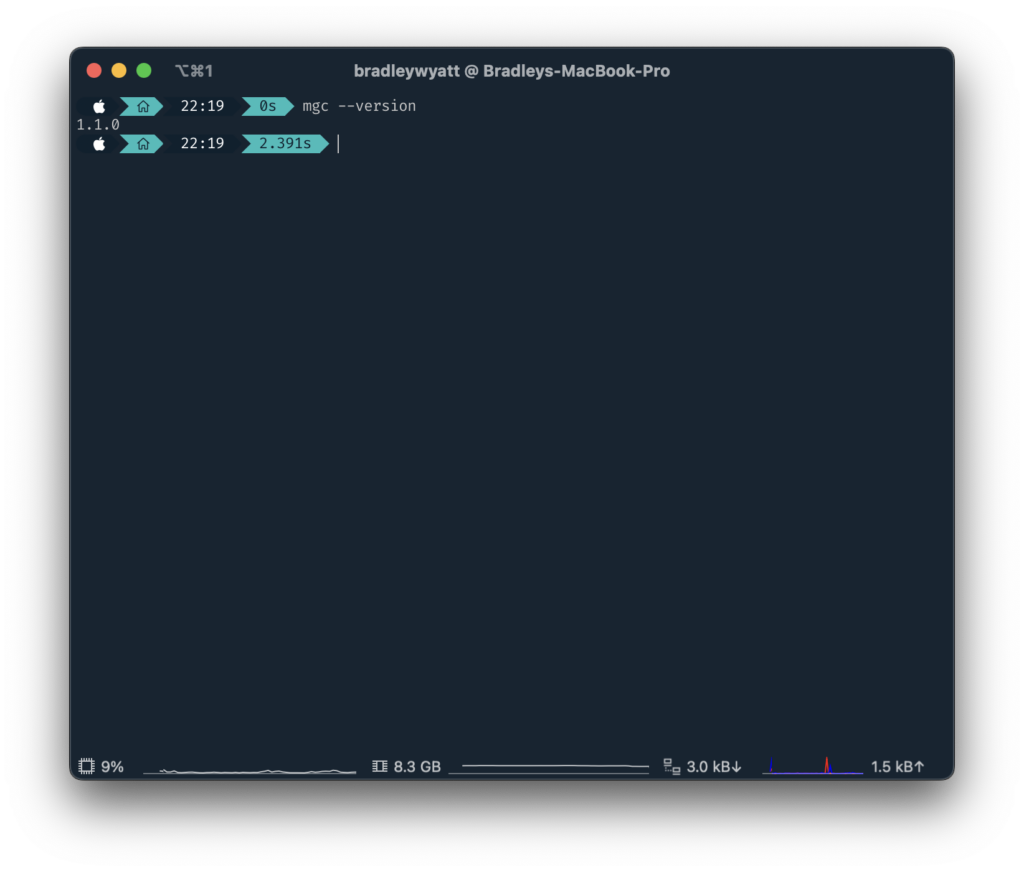
After the installation is completed, you can verify the installed version with the following command.
mgc --versionMacOS
Windows
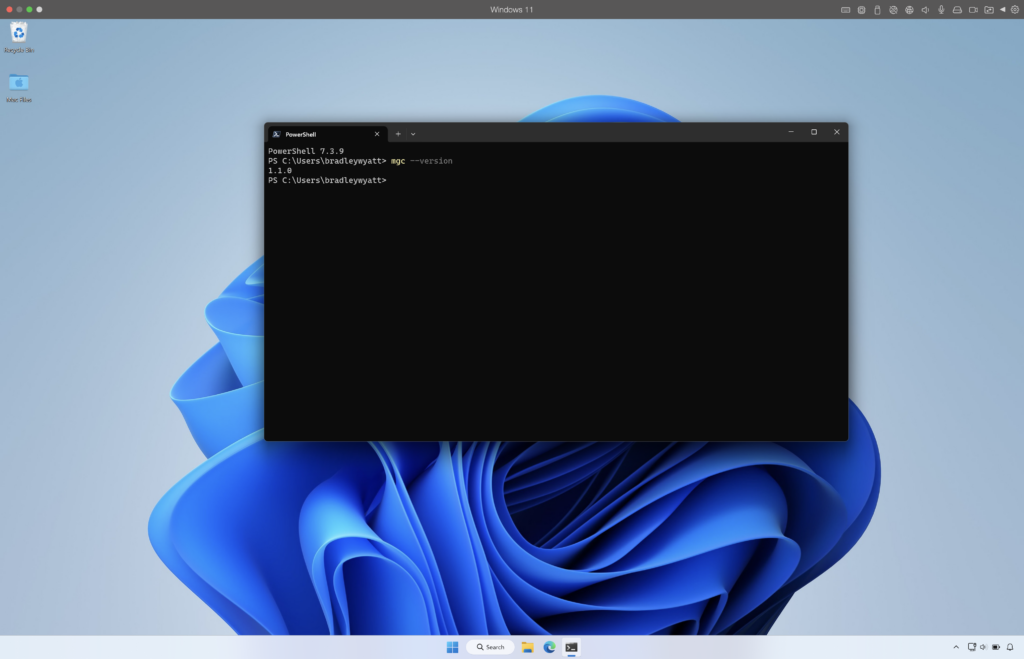
Updating the CLI
To update the CLI, download a newer version and extract into the directory containing the older version.
Uninstalling the CLI
Delete the extracted files from their location.
Get started with the Microsoft Graph command-line interface (CLI)
Authentication
The CLI supports two methods of authentication:
- delegated access (Device code flow and Interactive browser)
- app-only access (Client Secret, Environment Variables and Managed Identity)
For the purposes of this article, I will just touch on Device Code Flow and the Interactive Browser methods.
Device Code Flow
Device Code Flow authentication is the default method when just calling mgc login. With this method you will be instructed to go to a website and enter the code shown in the shell and authenticate with a user account within the browser.
mgc login 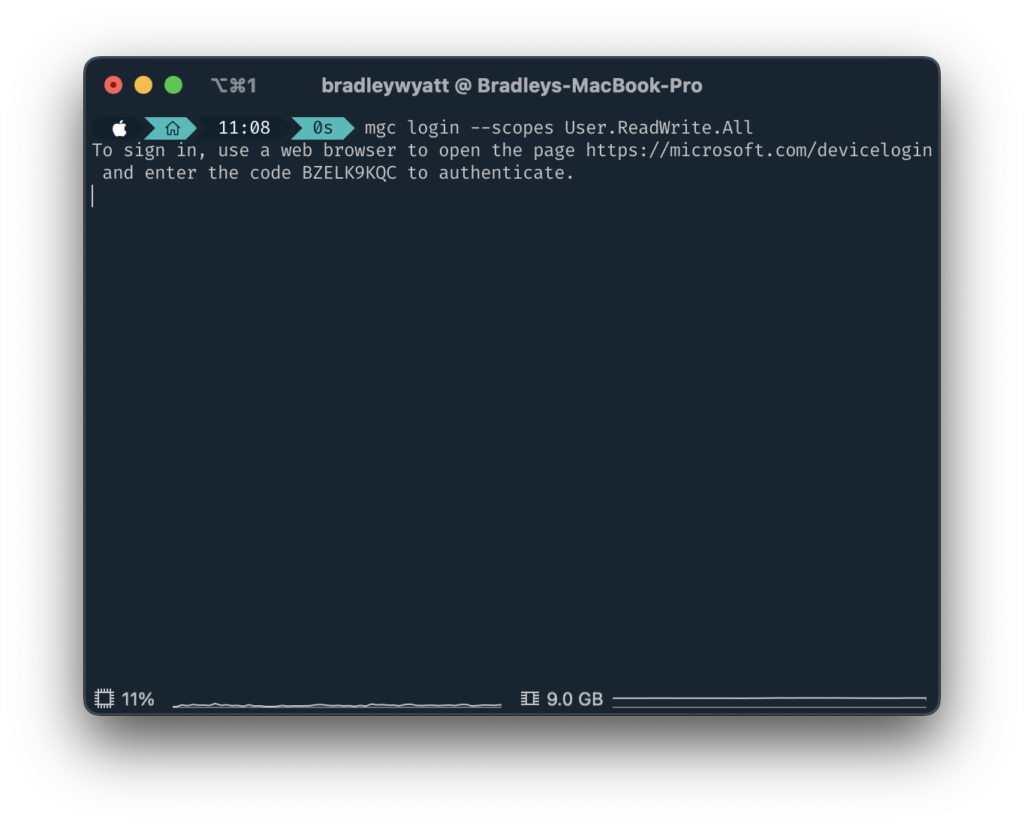
You can also login with device code flow with the following command:
mgc login --strategy DeviceCodeInteractive Browser
With the Interactive Browser method, it will automatically launch a web browser and you only need to sign in.
mgc login --strategy InteractiveBrowserScopes and Permissions
For the CLI to access data in Microsoft Graph, the user or administrator must grant it the permissions it needs. As a best practice, request the least privileged permissions that you need in order to access data and function correctly.
In order to see what type of permission you need, the Microsoft Graph documentation details the permissions for each access type. In the example below, we see what permissions you would need to get a user from the API.
| Permission type | Least privileged permissions | Higher privileged permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Delegated (work or school account) | User.Read | User.ReadWrite, User.ReadBasic.All, User.Read.All, User.ReadWrite.All, Directory.Read.All, Directory.ReadWrite.All |
| Delegated (personal Microsoft account) | User.Read | User.ReadWrite |
| Application | User.Read.All | User.ReadWrite.All, Directory.Read.All, Directory.ReadWrite.All |
When authenticating with the CLI you can call --scopes followed by the permission or permissions you need.
mgc login --scopes User.ReadWrite.All mgc login --scopes User.ReadWrite Mail.ReadWriteYou can call --scopes multiple times as well.
mgc login --scopes User.ReadWrite --scopes Mail.ReadWriteFor some permission types, you will be prompted to consent to the permissions requested.
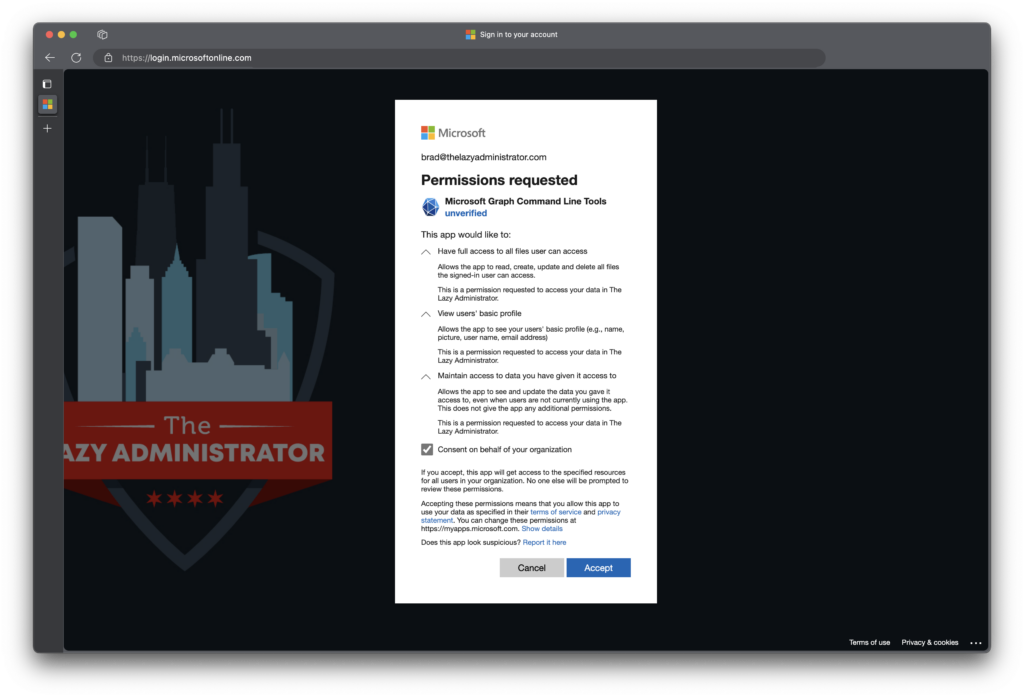
Debug
Using --Debug you can return detailed verbose output when running different commands. In the example below, I can see what is happening behind the scenes when trying to login.
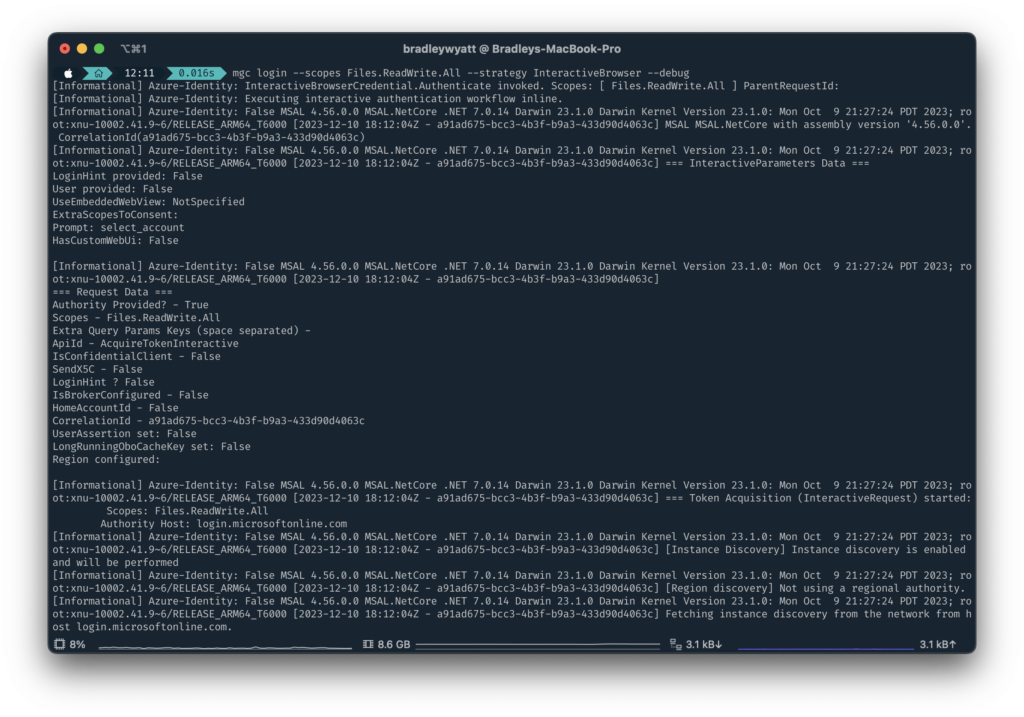
Help
The CLI provides detailed help that can be shown when running --h or --help. When running mgc --help to see what commands are available, I am returned the following:
| Command | Description |
| admin | Provides operations to manage the admin singleton. |
| agreement-acceptances | Provides operations to manage the collection of agreementAcceptance entities. |
| agreements | Provides operations to manage the collection of agreement entities. |
| app-catalogs | Provides operations to manage the appCatalogs singleton. |
| applications | Provides operations to manage the collection of application entities. |
| applications-with-app-id | Provides operations to manage the collection of application entities. |
| application-templates | Provides operations to manage the collection of applicationTemplate entities. |
| audit-logs | Provides operations to manage the auditLogRoot singleton. |
| authentication-method-configurations | Provides operations to manage the collection of authenticationMethodConfiguration entities. |
| authentication-methods-policy | Provides operations to manage the authenticationMethodsPolicy singleton. |
| certificate-based-auth-configuration | Provides operations to manage the collection of certificateBasedAuthConfiguration entities. |
| chats | Provides operations to manage the collection of chat entities. |
| communications | Provides operations to manage the cloudCommunications singleton. |
| compliance | Provides operations to manage the compliance singleton. |
| connections | Provides operations to manage the collection of externalConnection entities. |
| contacts | Provides operations to manage the collection of orgContact entities. |
| contracts | Provides operations to manage the collection of contract entities. |
| data-policy-operations | Provides operations to manage the collection of dataPolicyOperation entities. |
| device-app-management | Provides operations to manage the deviceAppManagement singleton. |
| device-management | Provides operations to manage the deviceManagement singleton. |
| devices | Provides operations to manage the collection of device entities. |
| devices-with-device-id | Provides operations to manage the collection of device entities. |
| directory | Provides operations to manage the directory singleton. |
| directory-objects | rovides operations to manage the collection of directoryObject entities. |
| directory-roles | Provides operations to manage the collection of directoryRole entities. |
| directory-roles-with-role-template-id | Provides operations to manage the collection of directoryRole entities. |
| directory-role-templates | Provides operations to manage the collection of directoryRoleTemplate entities. |
| domain-dns-records | Provides operations to manage the collection of domainDnsRecord entities. |
| domains | Provides operations to manage the collection of domain entities. |
| drives | Provides operations to manage the collection of drive entities. |
| education | Provides operations to manage the educationRoot singleton. |
| employee-experience | Provides operations to manage the employeeExperience singleton. |
| external | Provides operations to manage the external singleton. |
| filter-operators | Provides operations to manage the collection of filterOperatorSchema entities. |
| functions | Provides operations to manage the collection of attributeMappingFunctionSchema entities. |
| group-lifecycle-policies | Provides operations to manage the collection of groupLifecyclePolicy entities. |
| group-settings | Provides operations to manage the collection of groupSetting entities. |
| group-setting-templates | Provides operations to manage the collection of groupSettingTemplate entities. |
| groups | Provides operations to manage the collection of group entities. |
| identity-governance | Provides operations to manage the identityGovernance singleton. |
| identity | Provides operations to manage the identityContainer singleton. |
| identity-protection | Provides operations to manage the identityProtectionRoot singleton. |
| identity-providers | Provides operations to manage the collection of identityProvider entities. |
| information-protection | Provides operations to manage the informationProtection singleton. |
| invitations | Provides operations to manage the collection of invitation entities. |
| oauth2-permission-grants | Provides operations to manage the collection of oAuth2PermissionGrant entities. |
| organization | Provides operations to manage the collection of organization entities. |
| permission-grants | Provides operations to manage the collection of resourceSpecificPermissionGrant entities. |
| places | The places property |
| planner | Provides operations to manage the planner singleton. |
| policies | Provides operations to manage the policyRoot singleton. |
| Provides operations to manage the print singleton. | |
| privacy | Provides operations to manage the privacy singleton. |
| reports | Provides operations to manage the reportRoot singleton. |
| role-management | Provides operations to manage the roleManagement singleton. |
| schema-extensions | Provides operations to manage the collection of schemaExtension entities. |
| scoped-role-memberships | Provides operations to manage the collection of scopedRoleMembership entities. |
| search | Provides operations to manage the searchEntity singleton. |
| security | Provides operations to manage the security singleton. |
| service-principals | Provides operations to manage the collection of servicePrincipal entities. |
| service-principals-with-app-id | Provides operations to manage the collection of servicePrincipal entities. |
| shares | Provides operations to manage the collection of sharedDriveItem entities. |
| sites | Provides operations to manage the collection of site entities. |
| solutions | Provides operations to manage the solutionsRoot singleton. |
| subscribed-skus | Provides operations to manage the collection of subscribedSku entities. |
| subscriptions | Provides operations to manage the collection of subscription entities. |
| teams | Provides operations to manage the collection of team entities. |
| teams-templates | Provides operations to manage the collection of teamsTemplate entities. |
| teamwork | Provides operations to manage the teamwork singleton. |
| tenant-relationships | Provides operations to manage the tenantRelationship singleton. |
| me, users | Provides operations to manage the collection of user entities. |
| login | Login and store the session for use in subsequent commands |
| logout | Logout by deleting the stored session used by commands |
You can also view detailed information for each command. By running mgc users list --help I can see the detailed help for the users command.
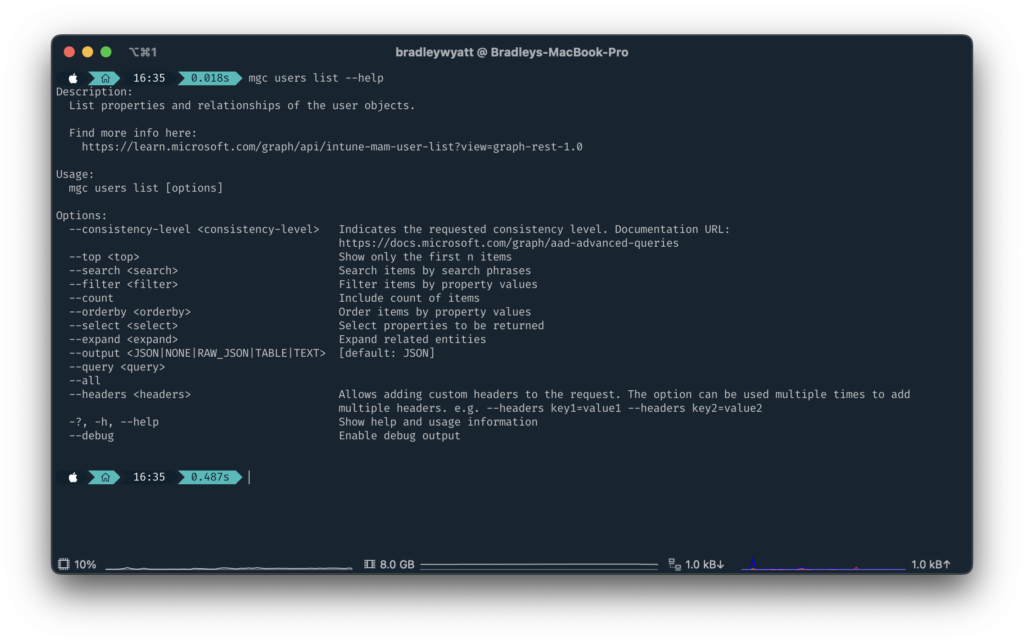
Formatted Output
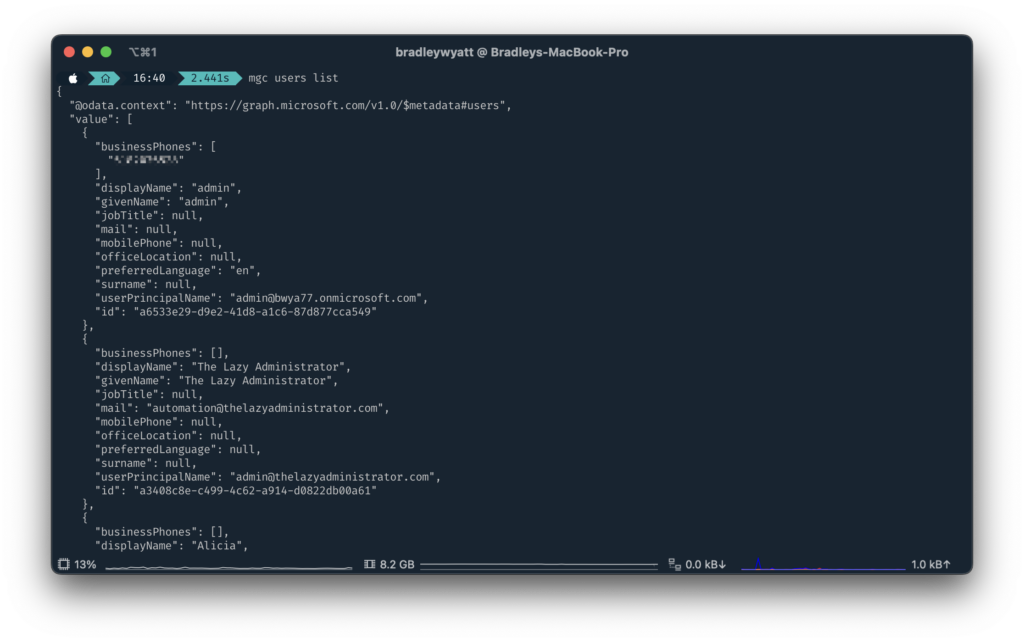
JSON
JSON is the default output when running a command. So, when running the command to get all users, ‘mgc users list‘ it will display the users in JSON format. You can also specify the JSON output by running:
mgc users list --output jsonYou can also export to raw json by using --output raw_json (not shown)
Table
Another output option is to format as a table. When outputting to a table it will auto format the table to the size of the shell window.
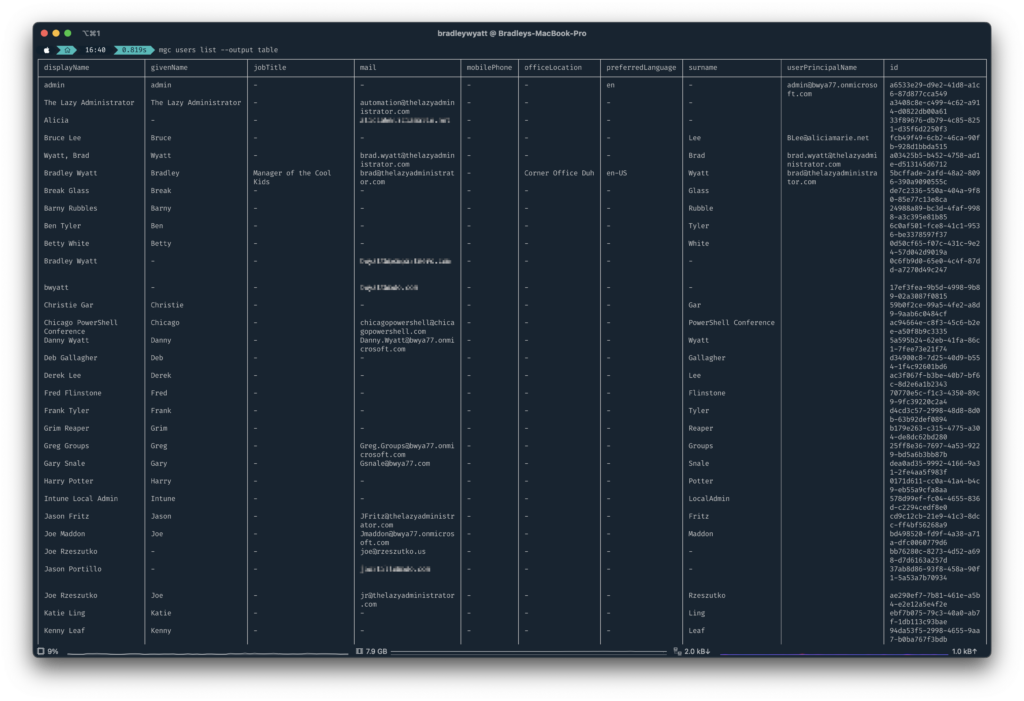
mgc users list --output tableText
The CLI also has the ability to export the results as a string of text using --output text
You can export to a table by running the following command:
Patch
Patch allows you to edit objects and update a property. In the example below I will be updating a user’s office location.
Bash:
mgc users patch --user-id "5bcffade-2afd-48a2-8096-390a9090555c" --body '{"officeLocation": "Carbondale"}'CMD:
mgc users patch --user-id "5bcffade-2afd-48a2-8096-390a9090555c" --body '"{""officeLocation"": ""NewLocation""}"Create
The create command allows you to create new objects using Microsoft Graph. Below I am creating a new Security Group called ‘cli-testing’
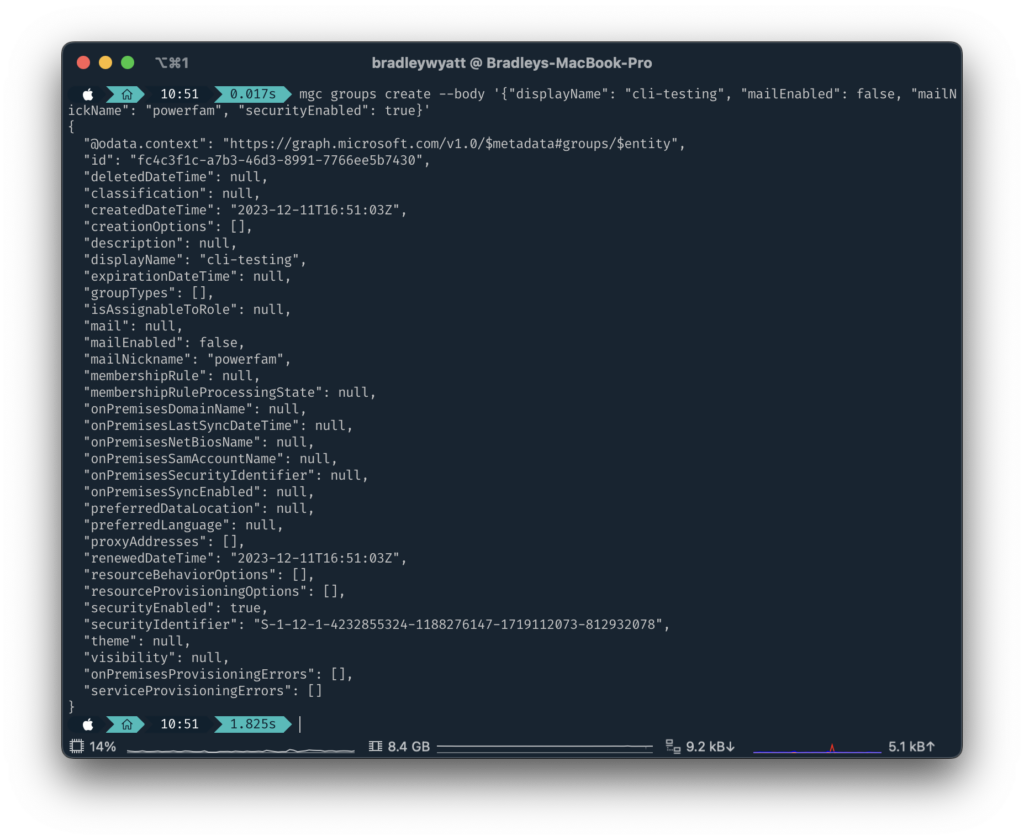
Bash
mgc groups create --body '{"displayName": "cli-testing", "mailEnabled": false, "mailNickName": "powerfam", "securityEnabled": true}'
PowerShell
$body = ConvertTo-Json '{"displayName": "cli-testing", "mailEnabled": false, "mailNickName": "powerfam", "securityEnabled": true}'
mgc groups create --body $bodyCMD
mgc groups create --body "{""displayName"": ""cli-testing"", ""mailEnabled"": false, ""mailNickName"": ""powerfam"", ""securityEnabled"": true}"Remove
The Remove command allows you to delete an object. Using remove I will remove the group that I just created using the create command.
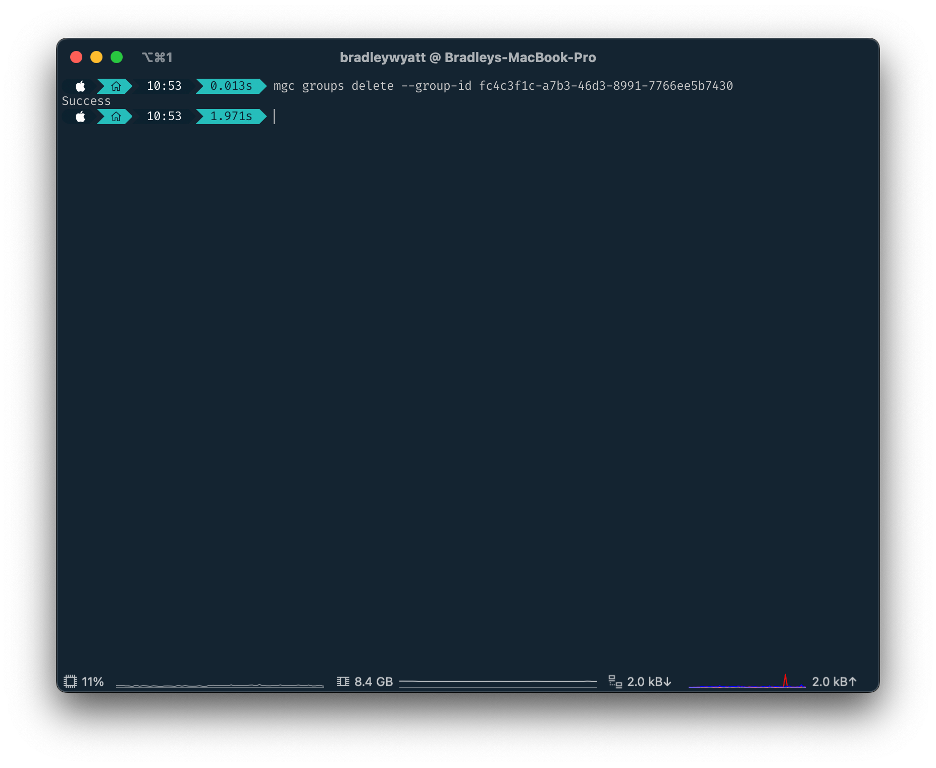
mgc groups delete --group-id fc4c3f1c-a7b3-46d3-8991-7766ee5b7430OData System Query Options
The Microsoft Graph CLI supports optional query parameters that you can use to specify and control the amount of data returned in a response. Below is a table or some of the available OData System Query Options and linked examples from Microsoft’s documentation.
| Name | Description |
| count | Retrieves the total count of matching resources. |
| expand | Retrieves related resources. |
| filter | Filters results (rows). |
| orderby | Orders results. |
| search | Returns results based on search criteria. |
| select | Filters properties (columns). |
| top | Sets the page size of results. |
Count
--count gives us a total count of the objects. In my example below I am returning 5 groups but using –count a new property, ‘@odata.count‘ is included that displays the total groups in my tenant which is 65.
mgc groups list --top 5 --count --consistency-level eventual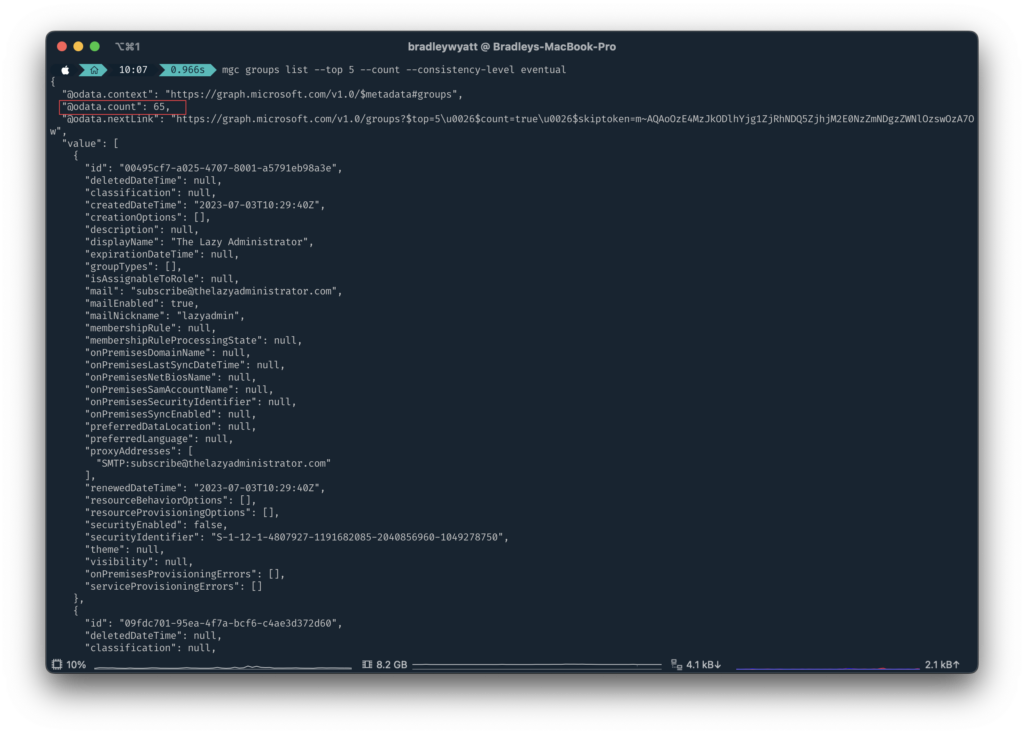
Expand
You can use --expand to include the expanded resource or collection referenced by a single relationship (navigation property) in your results. Only one relationship can be expanded in a single request.
In the below example I am returning all groups but expanding the members property of each group. This allows me to view the members of all my groups.
mgc groups list --expand members --allFilter
The Graph CLI supports the --filter to retrieve a subset of a collection or to retrieve relationships like members, memberOf, transitiveMembers, and transitiveMemberOf. This would be same format as a filter query parameter and Microsoft has a lot of great examples here.
Below are some examples with the returned value(s).
Get all users where the displayName begins with ‘Bradley’
mgc users list --filter "startswith(displayName,'Bradley')"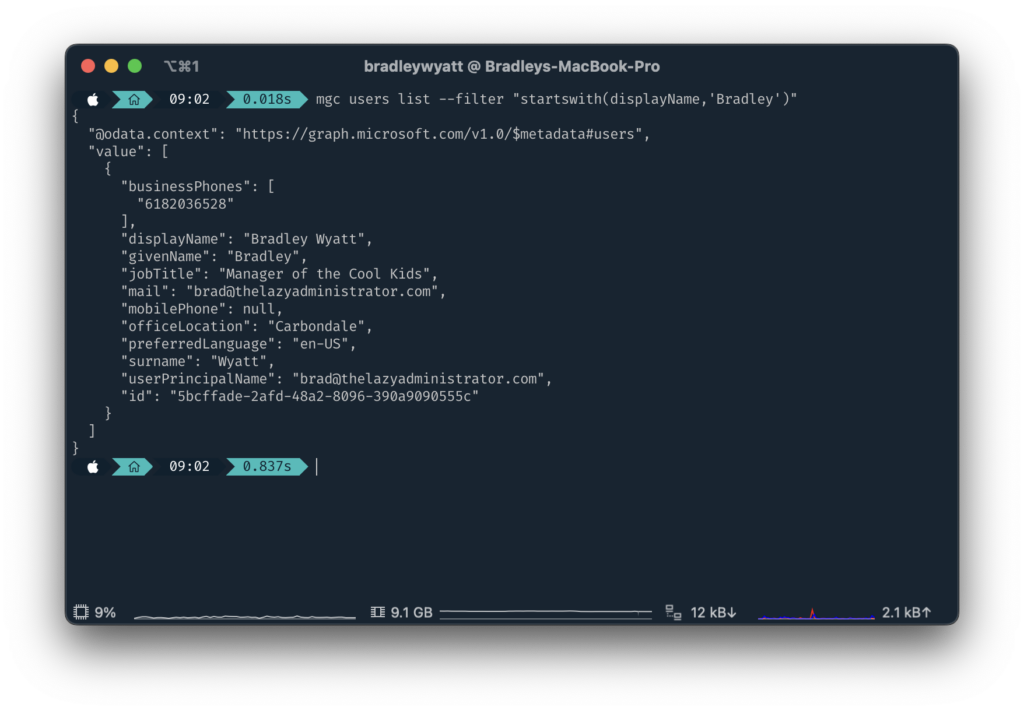
Get all emails for a user that were sent from a specific email address:
mgc users messages list --user-id 5bcffade-2afd-48a2-8096-390a9090555c --filter "from/emailAddress/address eq '[email protected]'"orderBy
orderBy allows you to order the results based on a specific property. In my example below I am getting all groups, selecting the properties, “displayName” and “mailEnabled” and then ordering the results by displayName.
mgc groups list --orderby displayName --select displayName,mailenabled --output table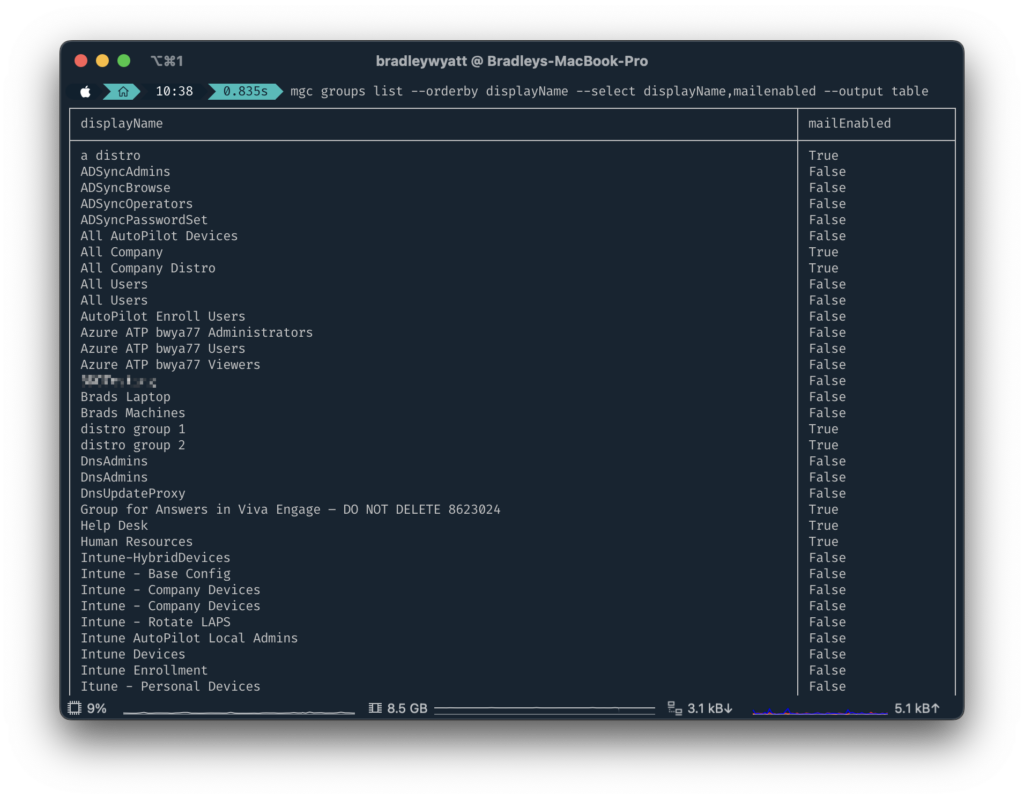
Search
--search allows you to restrict the results of a request to match a search criterion.
In my example below I am searching my mailbox for email messages with the word “Cloud PC”
mgc users messages list --user-id 5bcffade-2afd-48a2-8096-390a9090555c --search "Cloud PC"Select
Using the select statement, we can filter our results to only output properties that we care about.
In the below example I am using --filter to get emails that were sent to myself (my userid) and then looking for emails that were sent from [email protected], and then using --select, I am only selecting the properties, “receivedDateTime“,”hasAttachments“,”subject“,”bodyPreview“,”isread“,”isReadReceiptRequested“
mgc users messages list --user-id 5bcffade-2afd-48a2-8096-390a9090555c --filter "from/emailAddress/address eq '[email protected]'" --select "receivedDateTime","hasAttachments","subject","bodyPreview","isread","isReadReceiptRequested" --output table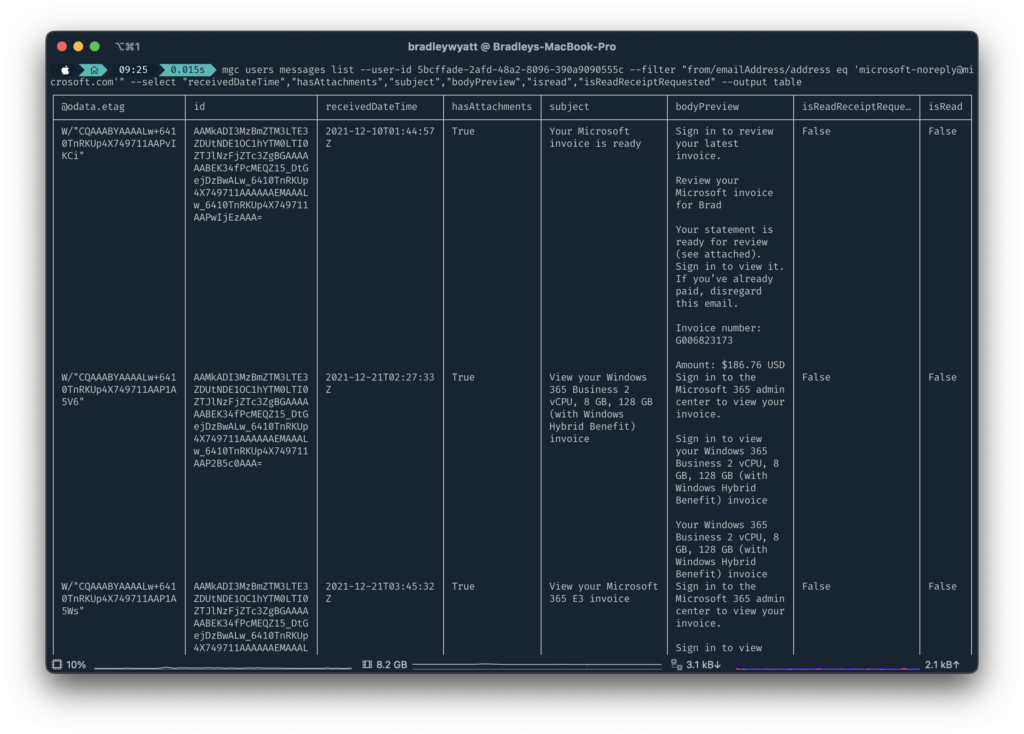
Top
–top returns the first n results. In my example I am getting all users but only returning the first 1 user.
mgc users list --top 1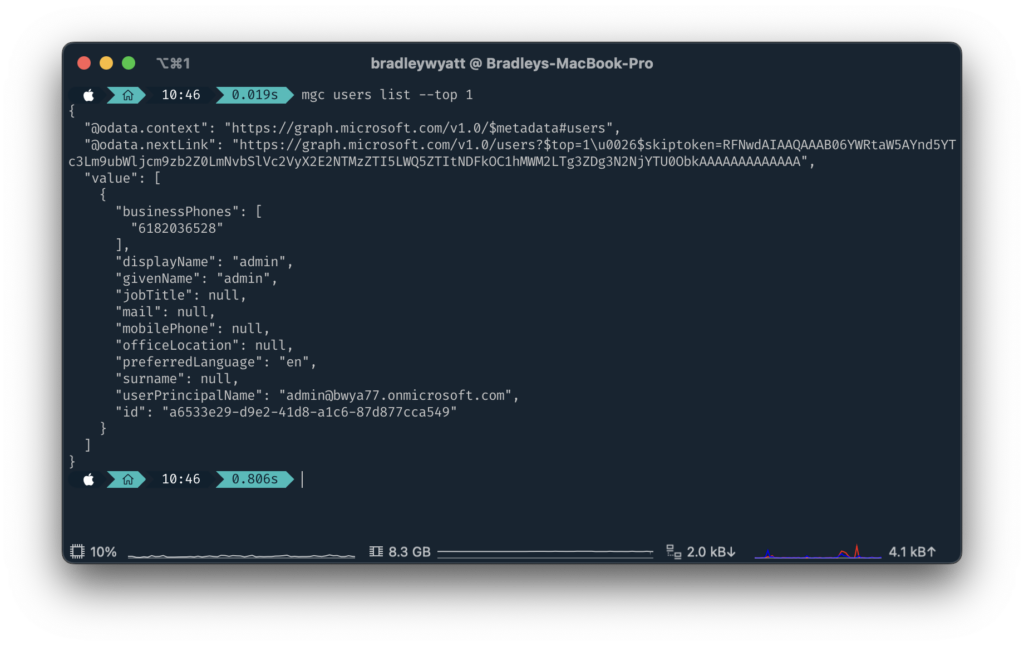
All
--all returns all object that you are looking for. In my example, I use –all to return all users within my tenant.
mgc users list --all
My name is Bradley Wyatt; I am a 5x Microsoft Most Valuable Professional (MVP) in Microsoft Azure and Microsoft 365. I have given talks at many different conferences, user groups, and companies throughout the United States, ranging from PowerShell to DevOps Security best practices, and I am the 2022 North American Outstanding Contribution to the Microsoft Community winner.
3 thoughts on “The Microsoft Graph Command-Line Interface (CLI)”
Great insights on the Microsoft Graph CLI! I appreciate how you broke down its features and use cases for administrators. It definitely simplifies tasks that used to require multiple steps. Looking forward to trying it out in my workflow!
Great post! I love the insights you shared about using the Microsoft Graph CLI for automation. It really simplifies tasks that usually take hours. Thanks for breaking it down so clearly!
Great insights on the Microsoft Graph CLI! I appreciate how you highlighted its benefits for streamlining administrative tasks. It’s definitely a game changer for those of us looking to enhance our productivity. Looking forward to trying out some of the commands you mentioned!